The most important results over the past 5 years
In the field of agriculture

The synthesis of the most important natural antioxidants of anthocyanins in winter rape plants, induced by the action of 5-aminolevulinic acid, has been discovered, which creates prospects for their use as a new alternative raw material source of anthocyanins for the needs of the food and pharmaceutical industries

A biotechnological collection of economically useful algae has been created. A waste-free and low-cost technology has been developed for the production of a biologically active feed additive based on algae (chlorella suspension) for the feed rations of farm animals and poultry
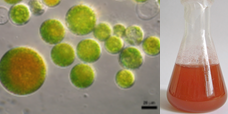
The principal possibility of using the Rose Bengal photosensitizer as an effective inducer of astaxanthin accumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis cells has been shown
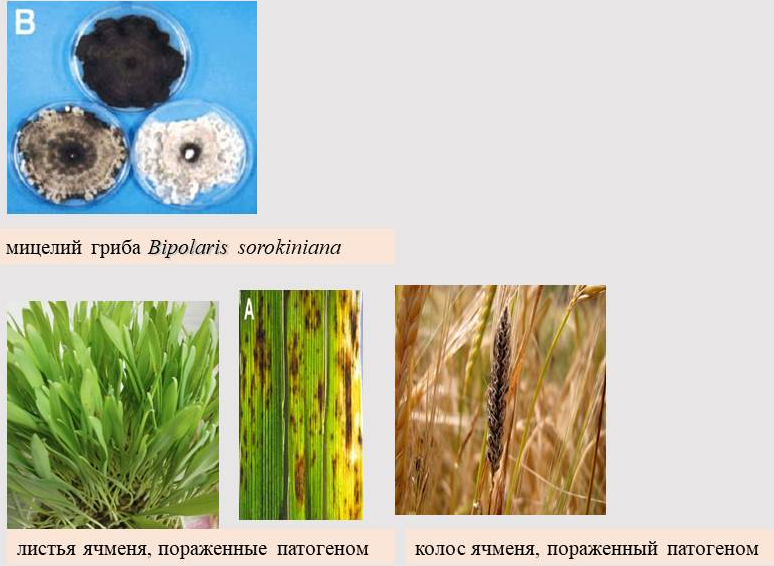

The molecular-membrane mechanisms of the response of spring barley plants to the combined action of hyperthermia and the pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.) Shoem are elucidated. - the causative agent of a widespread disease with dark brown spot. A method for testing phytopathogenic infection of spring barley with Bipolaris sorokinianа (Sacc.) Shoem has been scientifically substantiated. using indicators of oxidative stress, which greatly simplifies the diagnosis of the disease
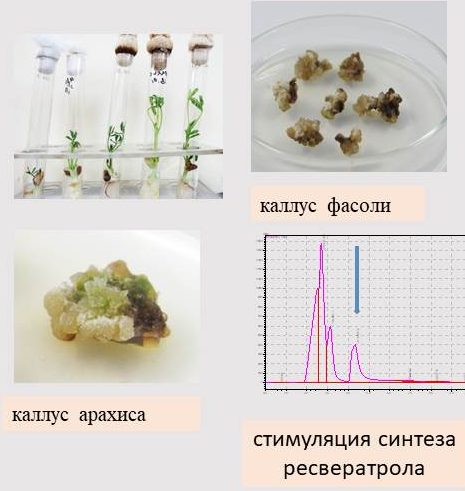
The possibility of metabolic regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in tissues of different plant species using exogenous salicylic acid (SA) has been theoretically substantiated and experimentally confirmed. The stimulating effect of SA on the total content of polyphenols and the accumulation of a powerful antioxidant - resveratrol in the tissue culture of peanuts was established, which can be used in the development of biotechnologies for obtaining plant substances with valuable antioxidant properties
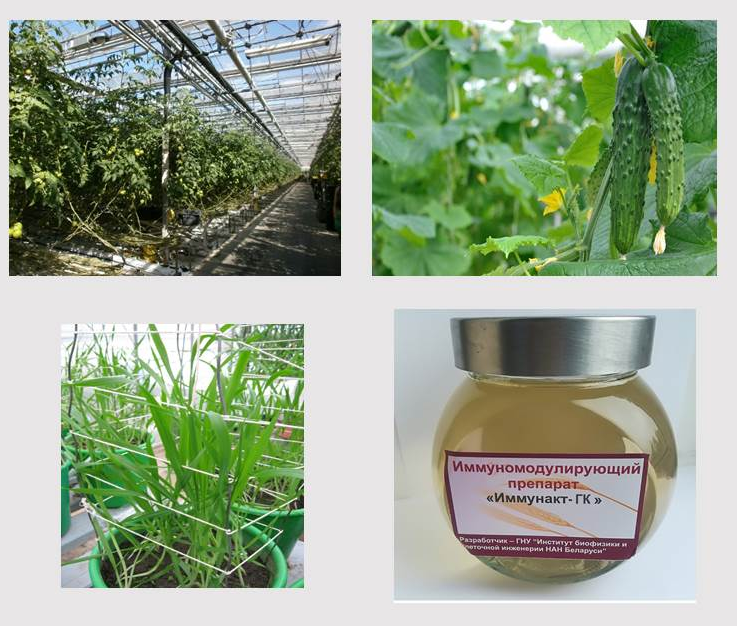

The physicochemical mechanisms of immunity of cultivated plants during pathogenesis are investigated. The use of β-aminobutyric acid, salicylic acid and its derivatives, β-1,3-glucan as immunomodulatory agents, inducing a complex of protective reactions in plant cells, including the activation of the salicylate signaling pathway, and increasing the resistance of vegetable, grain and industrial crops to phytopathogens

Research is underway on the characteristics of the formation of plant responses at the molecular-genetic level to the action of external environmental factors: biotic (plant resistance to the action of pathogenic organisms) and abiotic (development of the gravitropic reaction of aboveground plant organs). The search for potential candidate genes for the resistance of tomato and potato plants to late blight and other dangerous infectious diseases is being carried out. The features of the development of negative gravitropism in the aboveground organs of tomato plants at the transcriptome level are studied. Vertical structures are being developed for growing cultivated plants in artificial conditions
In the field medecine
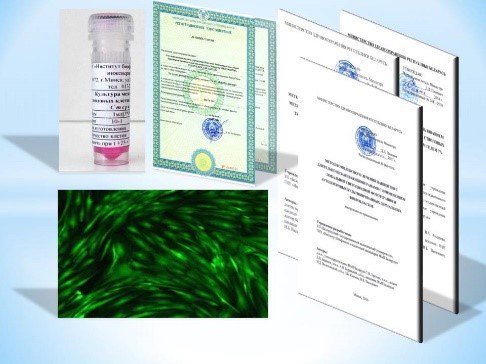
The metabolism of porphyrins in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has been studied and the mechanisms of action of hypoxia on the functional state of MSCs have been established. A biomedical cell product “Culture of mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue” has been developed, which is used in cell therapy of diseases. Based on the results of clinical studies, methods have been developed for the treatment of trophic ulcers and gum recessions (surgery, dentistry). Research is being carried out in the development of cellular therapy technologies in ophthalmology, urology, and gynecology. A biomedical cell product "Culture of human dermis fibroblasts" has been developed, which is used in the cell therapy of burns, long-term non-healing wounds, and cicatricial skin defects

In vitro studies are being carried out to determine the immunofunctional properties of dendritic cells. A biomedical cell product has been developed for the treatment of autoimmune and oncological diseases
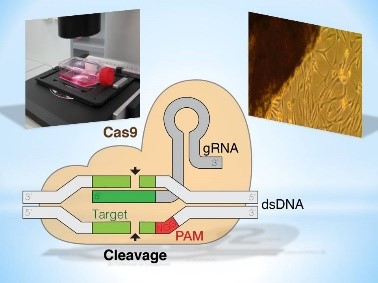
Research work has begun and is being carried out in new areas of cell biophysics: obtaining and using induced pluripotent cells in scientific research and medical practice, editing MSC genomes using CRISPR / CAS9 technology
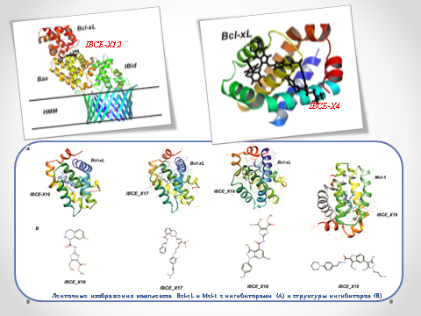
Research is carried out on structural bioinformatics, structural biophysics of the cell, computer design of drugs. A line of compounds with potential antitumor activity (IBCE-X1 - IBCE-X17) has been developed by the method of mathematical modeling
The redox-dependent regulation of the functional activity of proteins associated with the phenomenon of multiple drug resistance in human lymphocytes in normal and pathological conditions has been demonstrated. The role of cysteine-rich proteins of metallothioneins in maintaining cell viability in chronic B-lymphocytic leukemia has been established.
The mechanisms of eryptosis have been studied and the caspase-dependent pathway of its development in the population of erythrocytes of patients with iron deficiency anemia and anemia of chronic disease has been demonstrated.
The mechanism of the toxic effect of aluminum ions on human lymphocytes is shown, which is based on the processes of depolarization of mitochondrial membranes and the development of oxidative stress.
The role of an intracellular labile pool of zinc ions in the processes of maintaining the resistance of human erythrocytes to oxidative stress in normal conditions and in metabolic syndrome has been established.
A method for the detection of human B-lymphoblasts using 1D photonic nanostructures of zinc oxide has been developed, which will make it possible to create a portable analytical device based on an optical biosensor for the diagnosis of oncohematological diseases
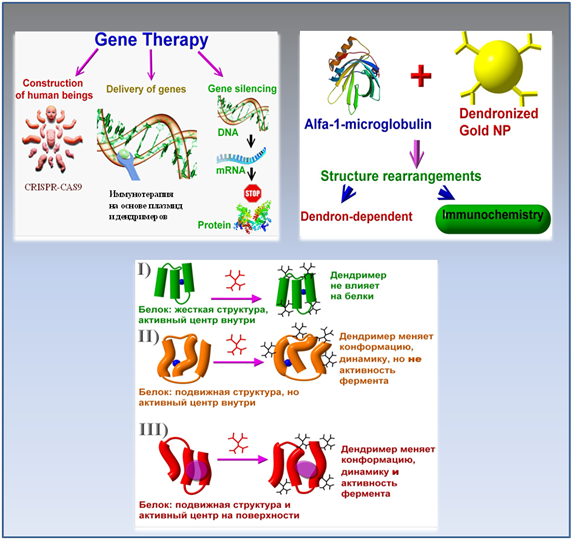
Biophysical mechanisms of interaction of dendrimers with proteins have been established. It has been shown that the “dendrimer – protein” binding occurs mainly on the surface of the protein globule and is determined by electrostatic interactions between the charged groups of the dendrimer and amino acid residues of the protein.
The mechanisms of interaction of dendrimers with proapoptotic miRNAs (siBcl2, siBCl-xL, siMcl-1) have been revealed. The complexes based on the dendrimer and a mixture of 3 miRNAs (cocktail) were efficiently transfected into HeLa and HL-60 cancer cells and caused a decrease in their viability.
It was found that the complex "miRNA-phosphorus dendrimer", added to cells in low concentrations, significantly enhances the anticancer effect of the chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil. The proposed method for gene therapy of malignant cells based on dendrimers and mixtures (cocktails) of siRNA can form the basis for the development of new methods of treating malignant neoplasms